“Spectroscopic Study of the Effects of Pressure Media on High-Pressure Phase Transitions in Natrolite”
- Authors
D. Liu, W. Lei, Z. Liu, Y. Lee*
- Journal
Journal of Physical Chemistry C
Vol.114(44), pp.18819-18824, 2010.10 - DOI
Abstract
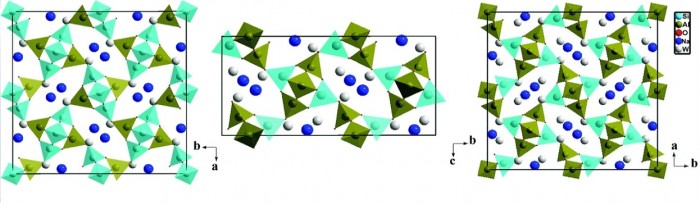
Structural phase transitions in natrolite have been investigated as a function of pressure and different hydrostatic media using micro-Raman scattering and synchrotron infrared (IR) spectroscopy. Natrolite undergoes two reversible phase transitions at 0.86 and 1.53 GPa under pure water pressure medium. These phase transitions are characterized by the changes in the vibrational frequencies of four- and eight-membered rings related to the variations in the bridging T−O−T angles and the geometry of the elliptical eight-ring channels under pressure. Concomitant to the changes in the framework vibrational modes, the number of the O−H stretching vibrational modes of natrolite changes as a result of the rearrangements of the hydrogen bonds in the channels caused by a successive increase in the hydration level under hydrostatic pressure. Similar phase transitions were also observed at relatively higher pressures (1.13 and 1.59 GPa) under alcohol−water pressure medium. Furthermore, no phase transition was found up to 2.52 GPa if a lower volume ratio of the alcohol−water to natrolite was employed. This indicates that the water content in the pressure media plays a crucial role in triggering the pressure-induced phase transitions in natrolite. In addition, the average of the mode Grüneisen parameters is calculated to be about 0.6, while the thermodynamic Grüneisen parameter is found to be 1.33. This might be attributed to the contrast in the rigidity between the TO4 tetrahedral primary building units and other flexible secondary building units in the natrolite framework upon compression and subsequent water insertion.